Can You Put Gel Polish on Fungal Nail?
Fungal Nail Infections and Gel Polish
Can you put gel polish on fungal nail – Fungal nail infections, also known as onychomycosis, are a common problem affecting millions worldwide. These infections can cause unsightly changes to the nails and, if left untreated, can lead to more serious complications. This article explores the nature of fungal nail infections, the potential impact of applying gel polish to infected nails, treatment options, and preventative measures.
Fungal Nail Infection Basics
Source: bmj.com
Fungal nail infections are caused by dermatophytes, yeasts, or molds that invade the nail plate. The infection can affect the toenails more frequently than fingernails due to the often-darker, warmer, and more moist environment in shoes.
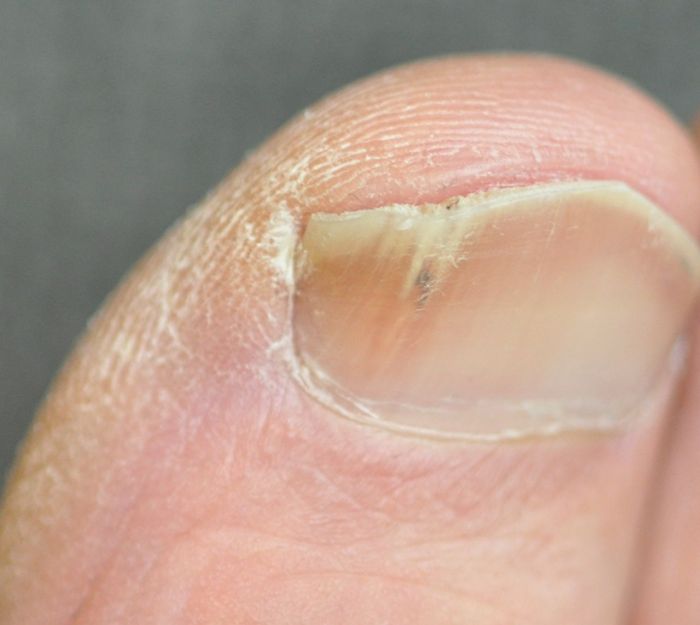
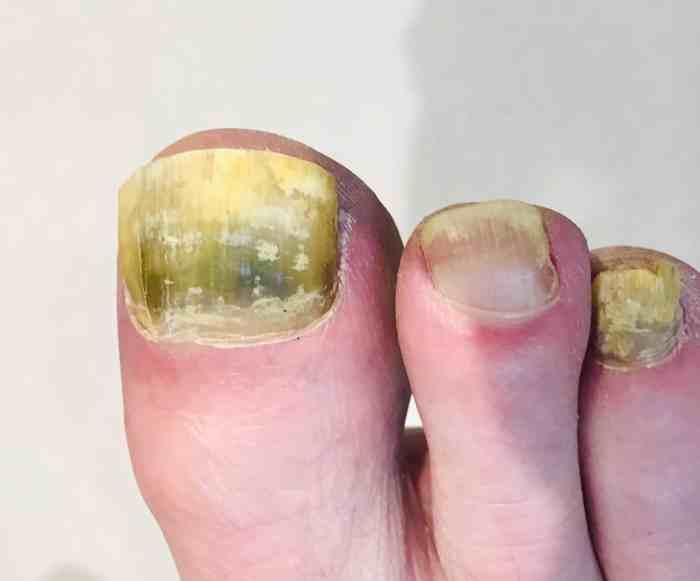
Common symptoms include discoloration (yellowing, browning, or whitening), thickening, crumbling, and separation of the nail from the nail bed (onycholysis). The nail may also become brittle and painful.
There are several types of fungal nail infections, classified based on the location and extent of the infection. Distinguishing between these types often requires a professional diagnosis.
Risk factors for developing fungal nail infections include having athlete’s foot, weakened immune systems, diabetes, psoriasis, and regularly wearing tight-fitting shoes or walking barefoot in damp public areas. Older individuals also tend to be more susceptible.
Visually identifying a fungal nail infection involves observing changes in nail color, texture, and shape. Look for discoloration (yellow, brown, green, or white), thickening, brittleness, separation from the nail bed, and debris under the nail. However, a definitive diagnosis requires professional evaluation.
Gel Polish Application and Fungal Nails
Applying gel polish to an already infected nail can exacerbate the problem. The polish traps moisture and creates a dark, warm environment that promotes fungal growth, potentially worsening the infection and masking its symptoms. This makes it harder to assess the infection’s progression.
Gel polish can interfere with the effectiveness of antifungal treatments. The polish acts as a barrier, preventing topical medications from reaching the infected area. It is generally recommended to remove gel polish before starting any antifungal treatment.
The effects of gel polish differ significantly between healthy and infected nails. On a healthy nail, gel polish provides a cosmetic enhancement with minimal impact. On an infected nail, it can worsen the infection and hinder treatment. This highlights the importance of treating the infection before applying any nail polish.
Gel polish can worsen or mask symptoms by trapping moisture, providing a breeding ground for the fungus, and obscuring visual changes indicative of the infection. This delay in diagnosis and treatment can lead to more severe and persistent infections.
Treatment Options for Fungal Nail Infections
Source: ftcdn.net
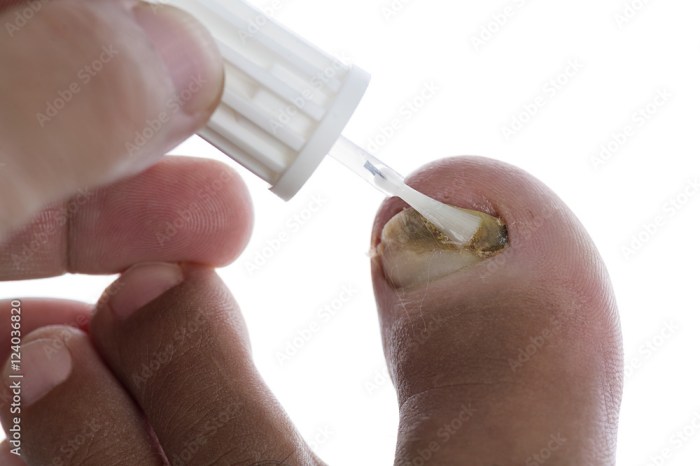
Several treatment options are available for fungal nail infections, each with varying effectiveness, side effects, and costs. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the infection and individual factors.
| Treatment Type | Effectiveness | Side Effects | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antifungal Creams (Topical) | Moderate, often requires prolonged use | Mild skin irritation, redness | Relatively low |
| Oral Antifungal Medications | Higher than topical treatments, but can take months to show improvement | Liver damage (rare but serious), nausea, headache, diarrhea | Moderate to high |
| Laser Therapy | Can be effective, but success rates vary | Minimal side effects, usually localized redness | High |
Antifungal topical creams are applied directly to the infected nail. The process involves cleaning the nail, applying a thin layer of cream, and repeating as directed. Consistency is key to success.
Potential side effects of oral antifungal medications can include gastrointestinal upset (nausea, diarrhea), headaches, and, in rare cases, more serious liver damage. Regular monitoring of liver function is sometimes recommended during treatment.
Laser therapy uses a low-level laser to target the fungus. It is generally considered a less invasive option with minimal side effects, although the cost can be substantial, and multiple sessions are often needed.
Nail Care Practices and Fungal Infections, Can you put gel polish on fungal nail
Source: com.au
Maintaining good nail hygiene is crucial in preventing fungal nail infections. This involves a combination of practices designed to keep nails clean, dry, and healthy.
Applying gel polish over a fungal nail infection isn’t recommended; it can trap moisture and worsen the condition. However, choosing a color like white, which some might consider a bold choice, can be a matter of personal preference. Interestingly, the perception of nail polish color varies; for example, to understand the male perspective on this, check out this article: what does white nail polish mean to guys.
Ultimately, treating the fungal infection is paramount before considering any cosmetic applications like gel polish.
- Keep nails trimmed short and filed smoothly to prevent snagging and injury.
- Wash your hands and feet regularly with soap and water, paying close attention to the nail areas.
- Dry your nails thoroughly after washing and showering, especially between the toes.
- Avoid walking barefoot in public places, such as locker rooms and showers.
- Wear breathable shoes and socks, changing them daily.
- Avoid sharing nail clippers, files, and other personal care items.
Recommended nail care products for infected nails include antifungal creams and gentle, non-irritating soaps. Avoid harsh chemicals and abrasive tools.
When to Seek Professional Help
Seeking professional medical advice is essential when self-treatment fails to improve the infection, or if the infection shows signs of worsening. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for optimal outcomes.
Consulting a doctor or podiatrist involves describing symptoms, undergoing a visual examination, and potentially undergoing a nail scraping or culture to confirm the diagnosis. They can then recommend the appropriate treatment plan.
Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for preventing the spread of the infection and minimizing potential complications. Delaying treatment can lead to more severe infections and increased treatment difficulty.
Situations where self-treatment is insufficient include persistent or worsening symptoms, signs of spreading infection, pain, or involvement of underlying medical conditions like diabetes.
Visual Representation of Infected vs. Healthy Nails
A healthy nail is typically smooth, pink, and firmly attached to the nail bed. An infected nail may exhibit a range of changes, including discoloration (yellow, brown, green, or white), thickening, crumbling, and separation from the nail bed (onycholysis). The nail may also appear brittle and distorted.
A healthy nail with gel polish will retain its smooth texture and natural pink hue underneath the polish. A fungal nail with gel polish may still exhibit discoloration, thickening, or separation, although the polish might mask some of these changes. The presence of debris or discoloration under the polish is a strong indicator of infection, even if it is less noticeable than on an unpolished nail.
Quick FAQs: Can You Put Gel Polish On Fungal Nail
Can I remove gel polish myself if I have a fungal nail infection?
It’s best to consult a podiatrist or dermatologist before attempting to remove gel polish from an infected nail. Improper removal can damage the already compromised nail.
Does gel polish prevent fungal nail infections?
No, gel polish does not prevent fungal nail infections. In fact, it can potentially worsen the infection by trapping moisture.
What are some home remedies for fungal nail infections?
While some home remedies might offer temporary relief, they are not a substitute for professional medical treatment. Consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.
How long does it take to treat a fungal nail infection?
Treatment time varies depending on the severity of the infection and the chosen treatment method. It can take several months or even years for complete recovery.